Investing is an essential component of wealth building, and two of the most common investment options are stocks and bonds. While both assets can help grow your wealth, they function very differently. Understanding the difference between stocks and bonds is crucial for making informed financial decisions. This article will break down their key differences, how they work, and which might be the best option for your investment strategy.

1. What Are Stocks?
Stocks represent ownership in a company. When you buy a stock, you are purchasing a small piece of that company, making you a shareholder. Companies issue stocks to raise capital for expansion, research, or other business needs.
Types of Stocks
There are two primary types of stocks:
- Common Stocks – These stocks give shareholders voting rights and potential dividends. However, they are more volatile, meaning their price can fluctuate significantly.
- Preferred Stocks – These offer fixed dividends and take priority over common stocks in case of liquidation. However, preferred shareholders usually don’t have voting rights.

2. What Are Bonds?
A bond is a fixed-income security that represents a loan made by an investor to a borrower, typically a corporation or government. The borrower agrees to pay back the principal amount with interest over a specified period.
Types of Bonds
- Government Bonds – Issued by federal or local governments. Examples include U.S. Treasury bonds, municipal bonds, and savings bonds.
- Corporate Bonds – Issued by businesses to fund their operations. They generally offer higher interest rates but carry more risk.
- Municipal Bonds – Offered by state or local governments for infrastructure projects.
- Treasury Bonds – Backed by the U.S. government, they are one of the safest investments.

3. Key Differences Between Stocks and Bonds
Understanding the difference between stocks and bonds involves looking at multiple factors, such as risk, return, and ownership.
Ownership vs. Debt
- Stocks: Represent ownership in a company.
- Bonds: Represent debt; the investor lends money to the issuer.
Risk and Return
- Stocks: High potential returns but higher risk due to market volatility.
- Bonds: More stable with fixed interest payments but lower returns.

Income Generation
- Stocks: Generate income primarily through dividends and capital appreciation.
- Bonds: Provide a predictable income stream through bond price appreciation and interest payments.
Market Volatility
- Stocks: Highly volatile; prices fluctuate based on market trends, company performance, and economic conditions.
Bonds: Less volatile, making them a safer investment during economic downturns.
Payout Priority
- Stocks: Shareholders are the last to receive payments if a company goes bankrupt.
- Bonds: Bondholders are paid before stockholders in case of liquidation.

4. How Stocks and Bonds Work in a Portfolio
A well-balanced portfolio includes a mix of stocks and bonds to reduce risk and maximize returns. Here’s how they complement each other:
- Growth Investing: Stocks offer potential for high growth but come with risks.
- Stability and Income: Bonds provide stability and consistent income.
- Diversification: Combining both helps reduce overall investment risk.
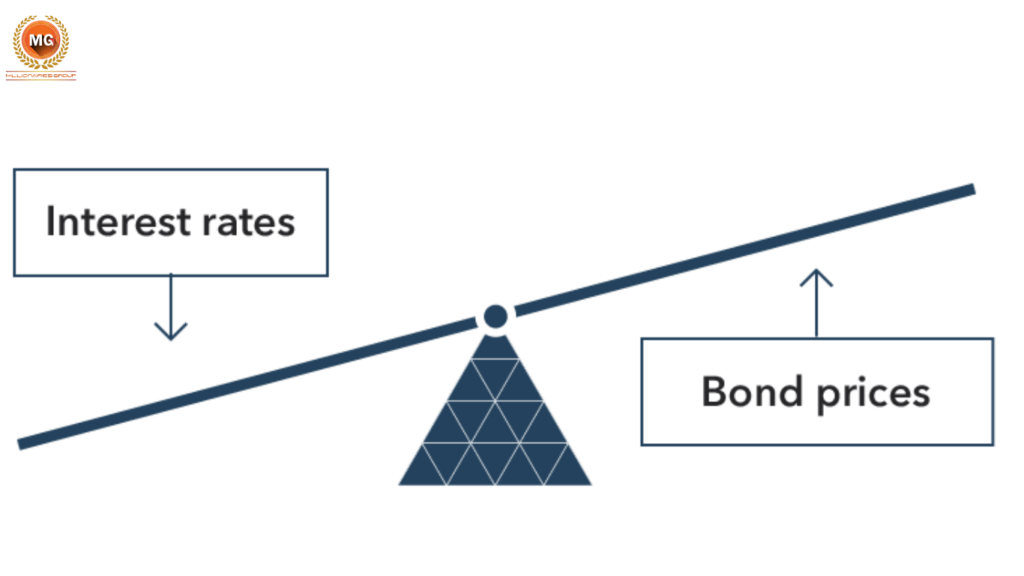
5. Bond Prices and Interest Rates
Bond price is influenced by interest rates. When interest rates rise, bond prices fall, and vice versa. This inverse relationship is crucial for bond investors to understand.
Yield to Maturity (YTM)
YTM is the total return anticipated on a bond if held until maturity. Investors use this metric to compare bond investments effectively.
6. Benefits of Investing in Stocks
- High Return Potential – Stocks have historically outperformed bonds in the long run.
- Liquidity – Stocks can be easily bought and sold in the stock market.
- Dividend Income – Many companies pay dividends, providing additional income.
7. Benefits of Investing in Bonds
- Predictable Returns – Bonds provide steady income through interest payments.
- Lower Risk – They are less volatile than stocks, making them ideal for conservative investors.
- Diversification – This can help balance a stock-heavy portfolio.

8. Drawbacks of Stocks and Bonds
Stocks
- High volatility – Prices can fluctuate significantly.
- No guaranteed returns – Market downturns can lead to losses.
- Dividends are not guaranteed – Companies can cut dividends anytime.
Bonds
- Lower returns – Typically offer lower returns than stocks.
- Interest rate risk – Rising rates can decrease bond value.
- Credit risk – Corporate bonds can default if the issuer faces financial trouble.
9. When to Invest in Stocks vs. Bonds
- If you have a long investment horizon and higher risk tolerance, stocks are a great option.
If you need a stable income and lower risk, bonds are preferable.
If you’re nearing retirement, increasing bond allocations can provide financial security.

Conclusion
Understanding the difference between stocks and bonds is essential for any investor. Stocks offer high growth potential but come with risks, while bonds provide stability and predictable income. A balanced mix of both in a portfolio can optimize returns while reducing risk. Whether you’re interested in bonds investing for security or stocks for growth, knowing their distinctions will help you make smarter financial decisions.
Are you ready to diversify your investment portfolio? Start by analyzing your financial goals and risk tolerance to decide the right mix of stocks and bonds that suits you best.
FOR A FREE STOCK MARKET SEMINAR VISIT HERE
CALLS @ 9986622277
Disclaimer
The information provided here is for general informational purposes only and should not be construed as financial advice. Investing in the stock market involves inherent risks, and there is no guarantee of profits or protection against losses. Before making any investment decisions, it is essential to conduct thorough research and seek advice from a qualified financial advisor or professional.
